
SSL VPN technology is seen by many as easier to configure and administer than IPSec. SSL VPN technology will work wherever one can gain access to HTTPS websites such as Internet Banking, Secure WebMail or Intranet sites.

Unfortunately it is through these public access networks where users’ need for VPN technology is at its greatest. Whilst IPSec uses a known protocol and associated port, this is often blocked on public access networks along with other tunnelling protocols. The single largest advantage SSL VPN technology has over traditional IPSec is the accessibility of the SSL library and access to port 443 TCP. This may be beneficial where time sensitive applications are required to function over a VPN connection for example a soft phone on a remote laptop.ĭTLS does not provide any reliability, oversize or re-sequencing technology: it is a simple connectionless protocol implementation with security features matching TLS (Figure 13). DTLS is a modified version of TLS which provides the same security and protection however is designed to work with UDP. Since the IETF took over the development of SSL, the terms SSL and TLS are often used interchangeably.Ĭlients can also negotiate a simultaneous DTLS (Datagram Transport Layer Security) connection to avoid possible latency with time sensitive applications like video and voice. TLS provides connection-oriented communication as a shim between the application layer and the transport layer to be used over a TCP connection. When SSL VPN clients negotiate a connection, they connect using TLS. SSL VPN technology is used exclusively for user connectivity where it provides an ideal solution for creating a VPN tunnel through restricted networks back to the home site. IPSec VPN technology is used for both end user and site-to-site connectivity.

There are several different variants of SSL VPN architecture and an increasing number of vendors and Open Source projects providing solutions. SSL VPN technology has grown in popularity in recent years and like its IPSec counterpart allows users to connect remotely back to their home organisation, obtaining access to restricted network resources.
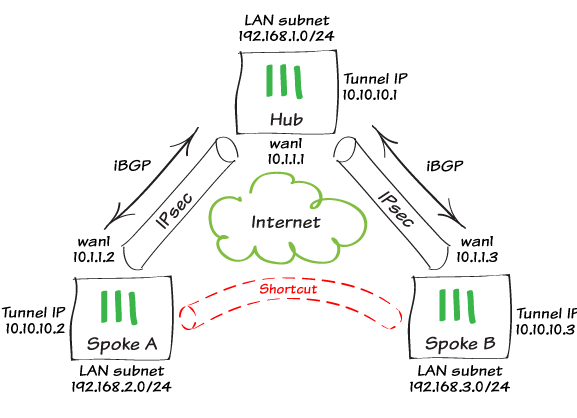

Multi-site Connectivity Advisory Service.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
